NIMH-funded examine used common screening, danger evaluation, and security planning to scale back suicide makes an attempt amongst grownup main care sufferers
December 30, 2024
• Analysis Spotlight
Suicide is a number one reason for dying in america and a serious public well being concern. Earlier analysis has proven that figuring out and serving to folks in danger for suicide throughout common care visits can assist stop it. Major care clinics are significantly necessary on this regard, as analysis has proven that over 40% of people that died by suicide had been seen on this setting within the month earlier than their dying.
A latest examine funded by the Nationwide Institute of Psychological Well being (NIMH) discovered that when main care clinics added suicide care practices to routine visits, suicide makes an attempt dropped by 25% within the 3 months after the go to. The findings spotlight how impactful it may be for main care clinics to take an lively function in stopping suicide and assist empower well being techniques to combine these practices into medical care.
What did the researchers do within the examine?
Major care clinicians display screen for melancholy throughout most care visits, and melancholy screeners typically embrace questions on suicide danger. Prior NIMH-supported analysis discovered that screening for suicidal ideas and behaviors adopted by transient security planning can cut back the chance of suicide makes an attempt.
Researchers led by Julie Angerhofer Richards, Ph.D., M.P.H. , on the Kaiser Permanente Washington Well being Analysis Institute aimed to see if integrating suicide care into routine grownup main care visits might stop subsequent suicide makes an attempt.
This examine analyzed secondary knowledge from a bigger built-in examine of the Nationwide Zero Suicide Mannequin . The great Zero Suicide method is the primary U.S. program linked to a considerable lower in suicides amongst behavioral well being sufferers. The analysis workforce beforehand examined this mannequin in a separate NIMH-funded examine at six well being techniques throughout america.
Earlier than the intervention, suppliers delivered care as common, which didn’t embrace population-based suicide screening or follow-up. The 22 collaborating clinics had been randomly assigned to begin delivering suicide care on staggered dates (4 months aside) over a 2-year interval. In the course of the examine, 333,593 sufferers had been seen for over 1.5 million main care visits.
Suicide care consisted of:
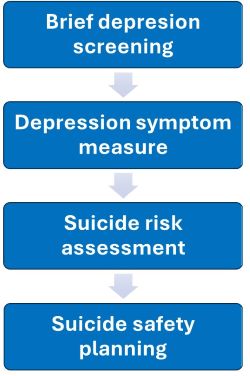
Despair screening: All sufferers accomplished a quick two-question melancholy screener, adopted by an extended melancholy symptom scale for many who scored optimistic on both query.Despair symptom scale: The screener was adopted by an extended melancholy symptom scale for sufferers who scored optimistic on both query.Suicide danger evaluation: Sufferers with ideas of self-harm or suicide accomplished a measure of suicidal ideas and behaviors.Suicide security planning: Sufferers who reported intent or plans for suicide within the final month had been referred to designated care employees, together with psychological well being social staff, for same-day suicide security planning. Security planning was a collaborative course of between sufferers and suppliers that concerned figuring out warning indicators, itemizing coping methods and helps, and creating secure environments to handle a suicidal disaster.
Three key methods supported the intervention:
Expert facilitators led trainings at every clinic and met with employees on an ongoing foundation to supply assist and clear up issues.Scientific determination assist, together with pre-visit reminders and go to prompts, got here from the clinics’ digital medical document system.Common efficiency monitoring of medical information reported on clinician charges of screening and evaluation.
The researchers in contrast clinics delivering suicide care to clinics delivering common care on:
Suppliers’ charges of documenting suicide danger evaluation and security planning within the medical document inside 2 weeks of an at-risk affected person’s main care visitPatients’ charges of suicide try or dying by suicide within the 90 days after their main care go to
What did the outcomes of the examine present?
Integrating suicide care into routine grownup main care visits led to considerably larger charges of suicide danger screening, evaluation, and collaborative security planning. The intervention in flip resulted in a 25% lower in suicide makes an attempt within the 90 days after a main care go to in comparison with common care clinics. Collectively, the outcomes reveal that integrating suicide prevention practices into grownup main care results in extra folks being screened for suicidal ideas and behaviors and fewer suicide makes an attempt as soon as they go away the clinic.
These findings assist NIMH’s prioritization of suicide prevention in well being care settings , with the final word aim of lowering the suicide charge in america. The examine supplies the important subsequent steps for suppliers and care groups in responding to suicidal considerations throughout medical follow, serving to save lives within the course of.
Reference
Richards, J. A., Cruz, M., Stewart, C., Lee, A. Okay., Ryan, T. C., Ahmedani, B. Okay., & Simon, G. E. (2024). Effectiveness of integrating suicide care in main care: Secondary evaluation of a stepped-wedge, cluster randomized implementation trial. Annals of Inner Drugs, 177(11), 1471–1482. https://doi.org/10.7326/M24-0024
Funding
If you happen to or somebody you already know is struggling or having ideas of suicide, name or textual content the 988 Suicide and Disaster Lifeline at 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org . In life-threatening conditions, name 911.
For extra info on suicide prevention, see:
Disclaimer
The Zero Suicide framework was developed on the Schooling Growth Middle (EDC) by the federally funded Suicide Prevention Useful resource Middle and the Nationwide Motion Alliance for Suicide Prevention. The Zero Suicide info and branding is freely obtainable on the Zero Suicide ToolkitSM , administered by EDC. No official endorsement by EDC is meant or needs to be inferred.








